p5 Trigonometric functions and oscillation (sin, cos) EMS Interactivity
The people of Emilia-Romagna love to eat meat, particularly pork. From the incredible cotechino in galera to milk-braised pork and stunning local delicacies, cook up some of the region's most famous dishes and see why everyone raves about them. Maiale al latte - milk-braised pork loin. by GIC Kitchen. Fried lamb chops.

Unit Circle Quick Lesson Printable PDF Chart · Matter of Math
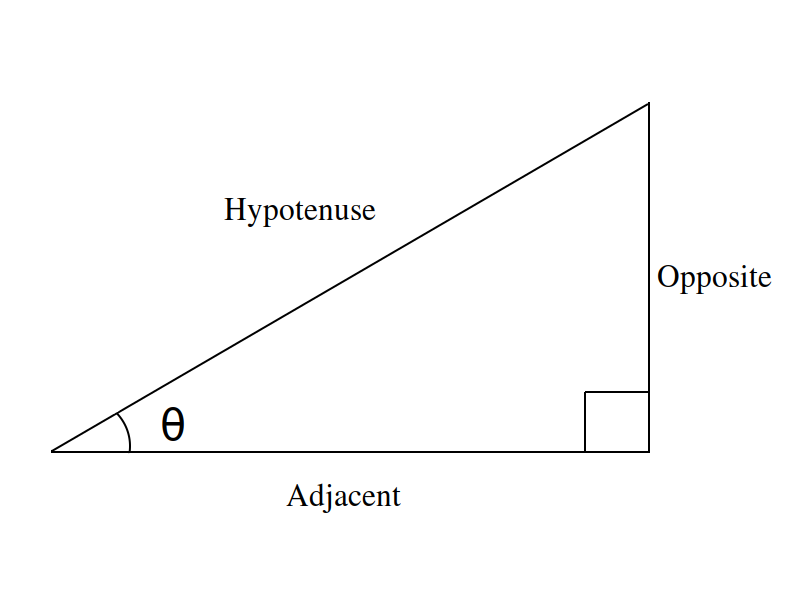
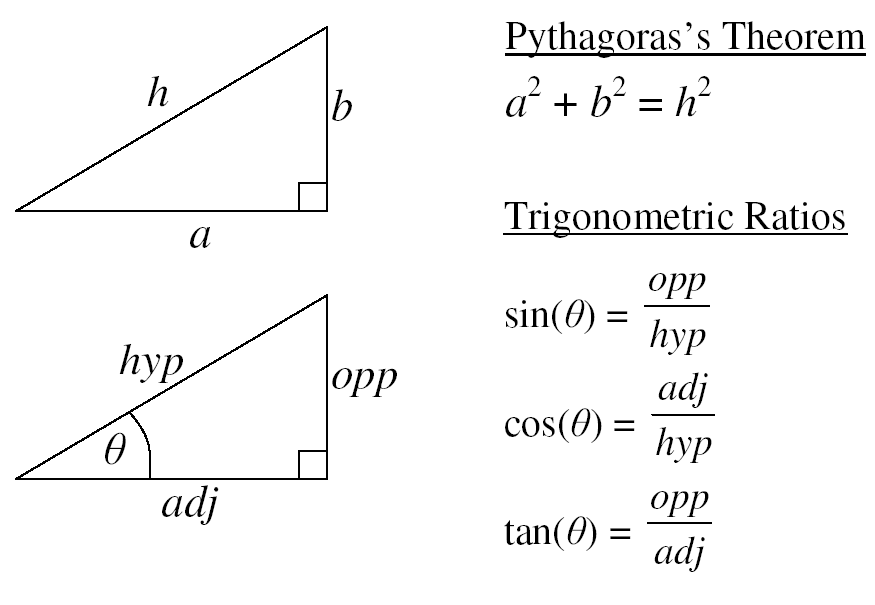
Sine, Cosine and Tangent (often shortened to sin, cos and tan) are each a ratio of sides of a right angled triangle: For a given angle θ each ratio stays the same no matter how big or small the triangle is To calculate them: Divide the length of one side by another side Example: What is the sine of 35°?
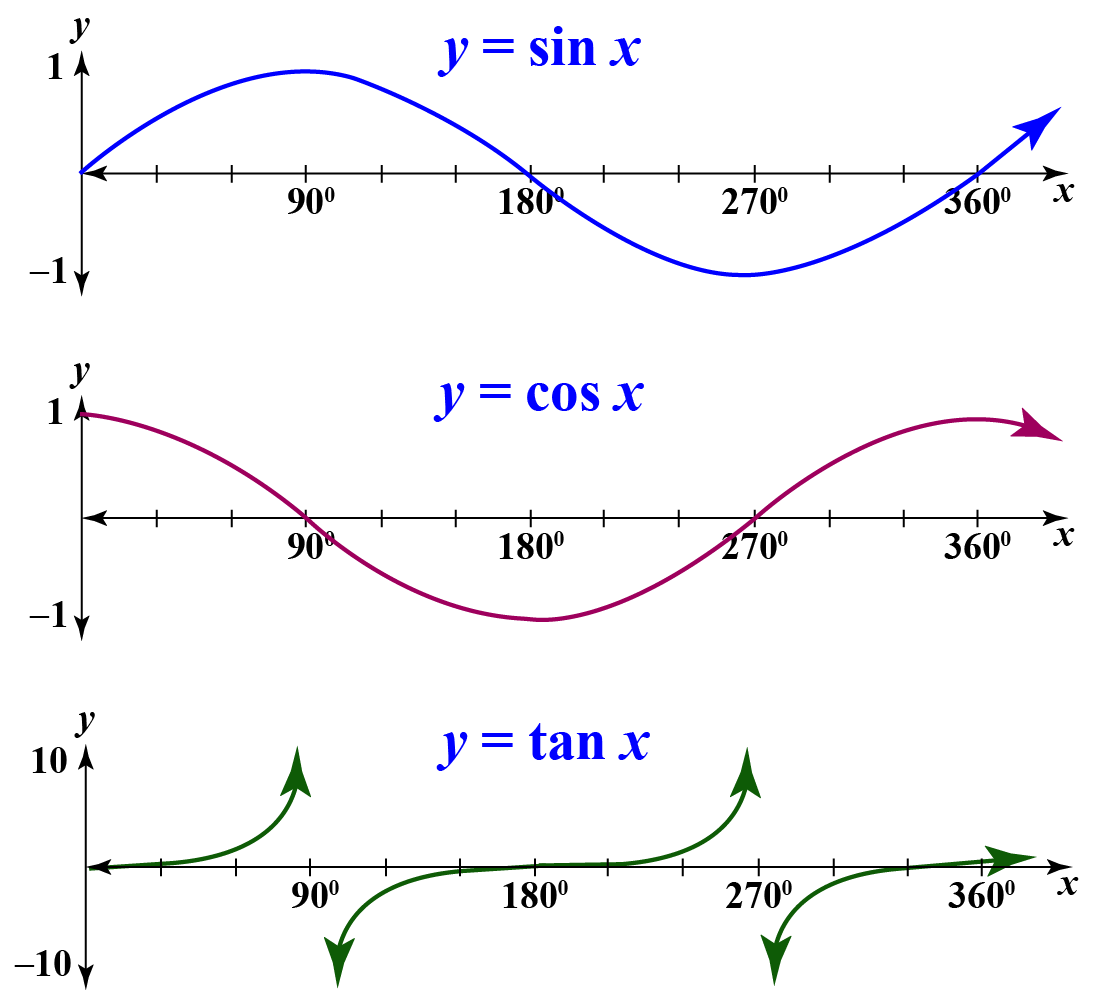
Tangent Function Tan Graph Solved Examples Cuemath
Sines Cosines Tangents Cotangents Pythagorean theorem Calculus Trigonometric substitution Integrals ( inverse functions) Derivatives v t e In trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of the equality are defined.
Notes on everything Sine, Cosine, Tangent
🔎 Trigonometric functions (sin, cos, tan) are all ratios. Therefore, you can find the missing terms using nothing else but our ratio calculator! Trigonometry has plenty of applications: from everyday life problems such as calculating the height or distance between objects to the satellite navigation system, astronomy, and geography.
Sin Cos Tan Graphs / Graphs of Hyperbolic functions Sin, Cos and Tan YouTube / The following
Sine is the ratio of Opposite / Hypotenuse: sin (45°) = Opposite Hypotenuse Get a calculator, type in "45", then the "sin" key: sin (45°) = 0.7071.

Trigonometry
Sine, Cosine and Tangent The three main functions in trigonometry are Sine, Cosine and Tangent. They are just the length of one side divided by another For a right triangle with an angle θ : For a given angle θ each ratio stays the same no matter how big or small the triangle is When we divide Sine by Cosine we get:
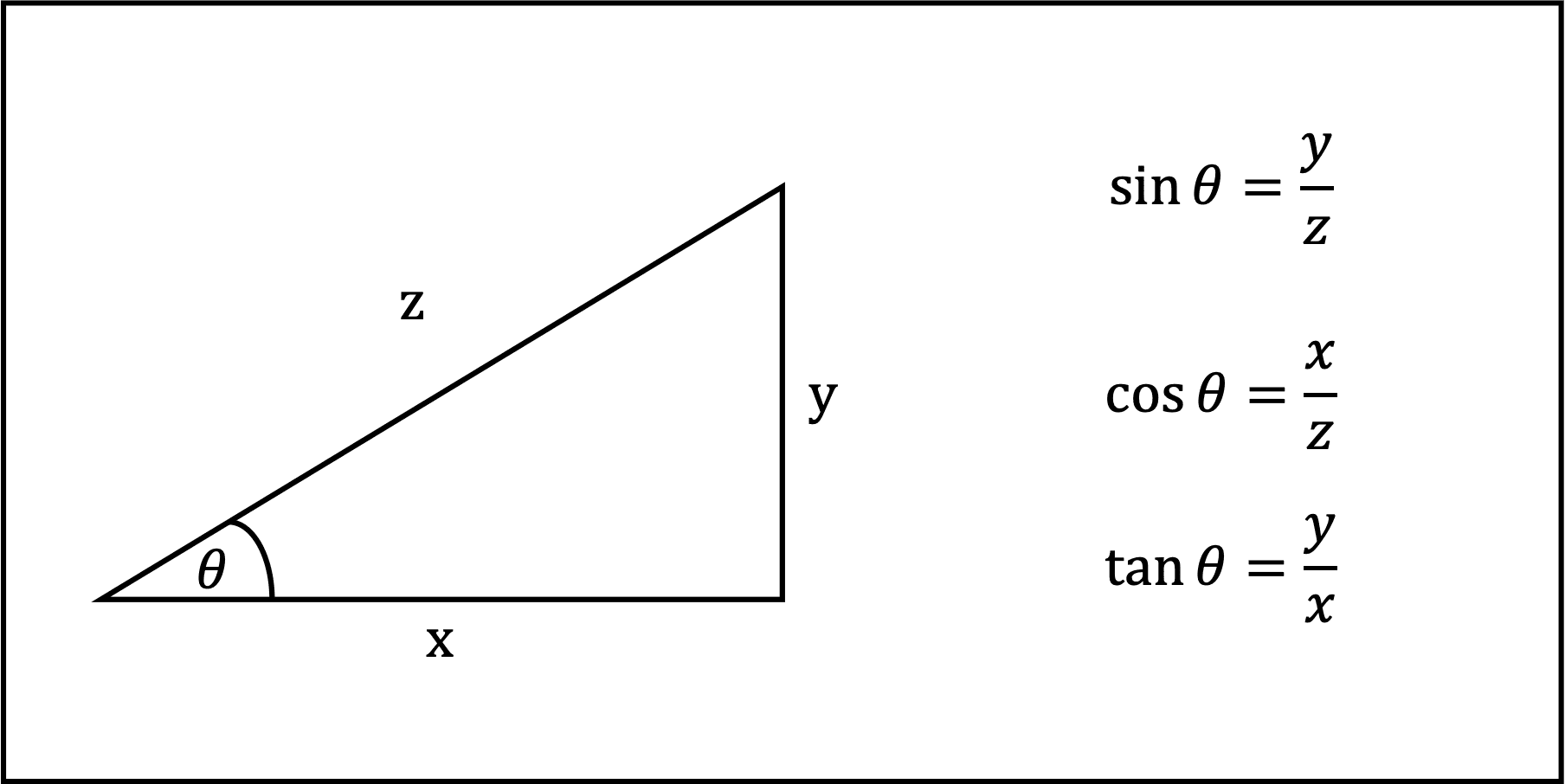
Trigonometric (Sin Cos Tan) Table 0360 Degrees (Downloadable) and How to Learn from It
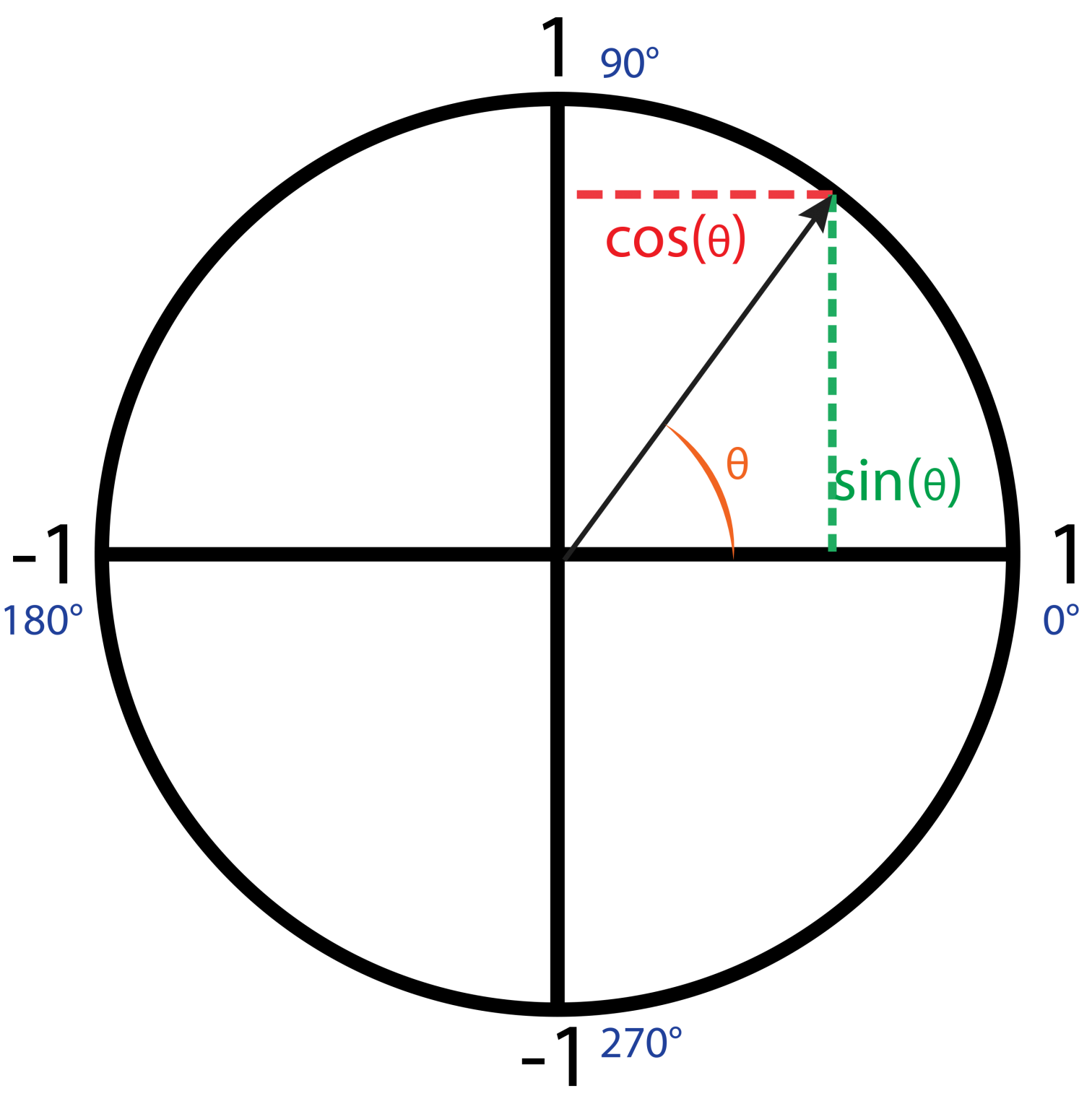
1 + cot 2 ( t) = csc 2 ( t) Advertisement Note that the three identities above all involve squaring and the number 1. You can see the Pythagorean-Thereom relationship clearly if you consider the unit circle, where the angle is t, the "opposite" side is sin (t) = y, the "adjacent" side is cos (t) = x, and the hypotenuse is 1.

Basic trigonometric identities
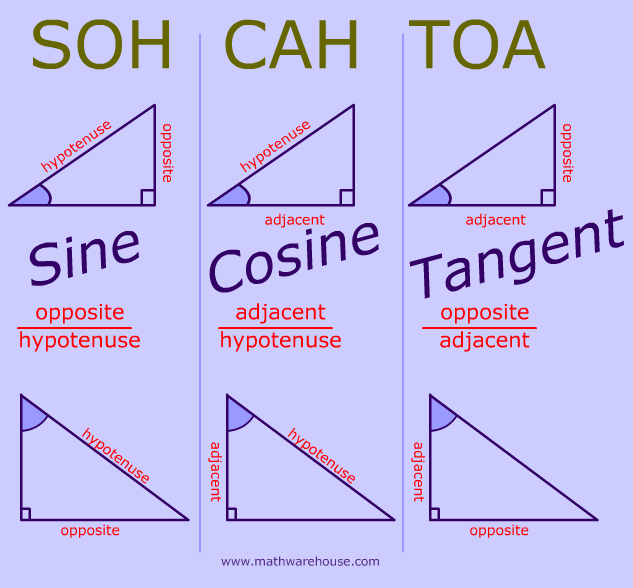
Sin, cos, and tan are trigonometric ratios that relate the angles and sides of right triangles. Sin is the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse, cos is the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse, and tan is the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side. They are often written as sin (x), cos (x), and tan (x), where x is an.
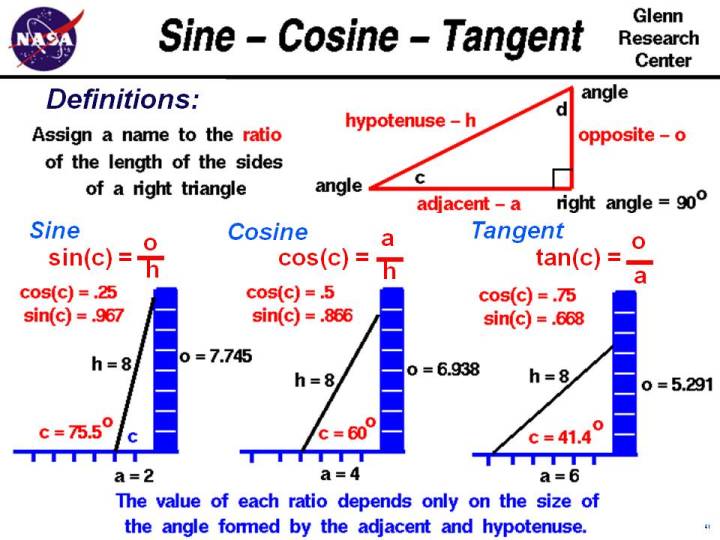
And now for the details! Sine, Cosine and Tangent are all based on a Right-Angled Triangle. They are very similar functions. so we will look at the Sine Function and then Inverse Sine to learn what it is all about.. Sine Function. The Sine of angle θ is:. the length of the side Opposite angle θ; divided by the length of the Hypotenuse; Or more simply:
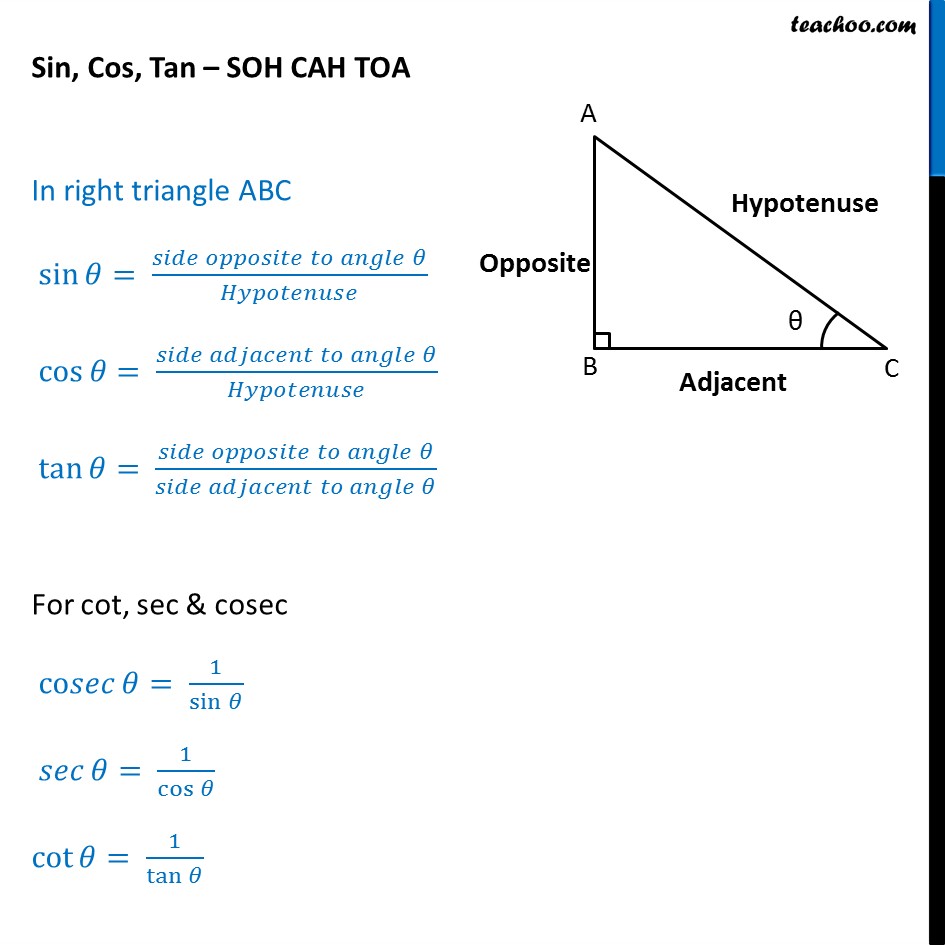
What are sin cos tan? SOHCAHTOA With Examples Teachoo
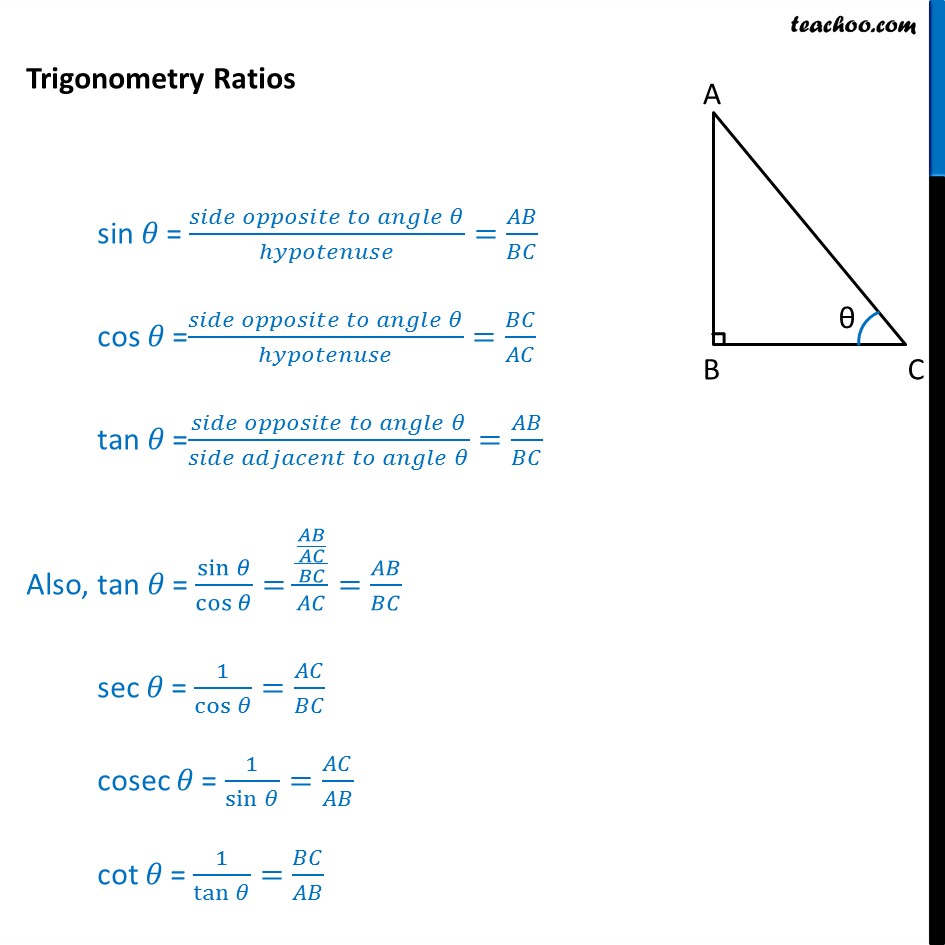
Sin Cos Tan Formulas The important sin cos tan formulas (with respect to the above figure) are: sin A = Opposite side/Hypotenuse = BC/AB cos A = Adjacent side/Hypotenuse = AC/AB tan A = Opposite side/Adjacent side = BC/AC We can derive some other sin cos tan formulas using these definitions of sin, cos, and tan functions.

How to Remember the Trigonometric Table 9 Steps (with Pictures)
Sine and cosine are written using functional notation with the abbreviations sin and cos.. Often, if the argument is simple enough, the function value will be written without parentheses, as sin θ rather than as sin(θ).. Each of sine and cosine is a function of an angle, which is usually expressed in terms of radians or degrees.Except where explicitly stated otherwise, this article assumes.

Sin, Cos, Tan
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics concerned with relationships between angles and ratios of lengths. The field emerged in the Hellenistic world during the 3rd century BC from applications of geometry to astronomical studies. The Greeks focused on the calculation of chords, while mathematicians in India created the earliest-known tables of.
Sine, Cosine, Tangent, explained and with Examples and practice identifying opposite, adjacent
Sin Cos Tan Values In trigonometry, sin cos and tan values are the primary functions we consider while solving trigonometric problems. These trigonometry values are used to measure the angles and sides of a right-angle triangle. Apart from sine, cosine and tangent values, the other three major values are cotangent, secant and cosecant. 42,598
Section 4 Sine And Cosine Rule
About Transcript Trigonometric identities like sin²θ+cos²θ=1 can be used to rewrite expressions in a different, more convenient way. For example, (1-sin²θ) (cos²θ) can be rewritten as (cos²θ) (cos²θ), and then as cos⁴θ. Created by Sal Khan. Questions Tips & Thanks Want to join the conversation? Sort by: Top Voted E Man 9 years ago

Sine, Cosine and Tangent Trigonometry, Tangent, Physics
Today, the most common versions of these abbreviations are "sin" for sine, "cos" for cosine, "tan" or "tg" for tangent, "sec" for secant, "csc" or "cosec" for cosecant, and "cot" or "ctg" for cotangent.

What are sin cos tan? SOHCAHTOA With Examples Teachoo
tan(x y) = (tan x tan y) / (1 tan x tan y) . sin(2x) = 2 sin x cos x cos(2x) = cos ^2 (x) - sin ^2 (x) = 2 cos ^2 (x) - 1 = 1 - 2 sin ^2 (x) . tan(2x) = 2 tan(x) / (1.